The hexagono, commonly referred to as a hexagon, is a six-sided polygon celebrated for its symmetry, efficiency, and versatility. From its role in nature to its applications in design and technology, the hexagon is a cornerstone of both geometric principles and practical usage. This article delves deeply into the geometry of the hexagono, its natural and industrial significance, and why it continues to captivate designers, architects, and scientists alike.
What is a Hexagono?
A hexagono is a polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles. It belongs to the family of regular polygons and holds a special place in geometry due to its perfect symmetry. This shape is unique because it tessellates, or tiles, perfectly without leaving gaps—ideal for creating efficient, compact, and visually appealing designs.
Key Properties of a Hexagono
- Sides and Angles: Six sides of equal length and internal angles measuring 120 degrees.
- Tessellation: Ability to fit together without gaps, a rare property among polygons.
- Symmetry: Exhibits rotational and reflective symmetry, making it balanced and aesthetically pleasing.
The Geometry of Hexagono: An In-Depth Look
The geometry of a hexagono is not just about its six sides; it’s about its relationship with other polygons, its mathematical properties, and its applications in spatial reasoning.
Mathematical Properties
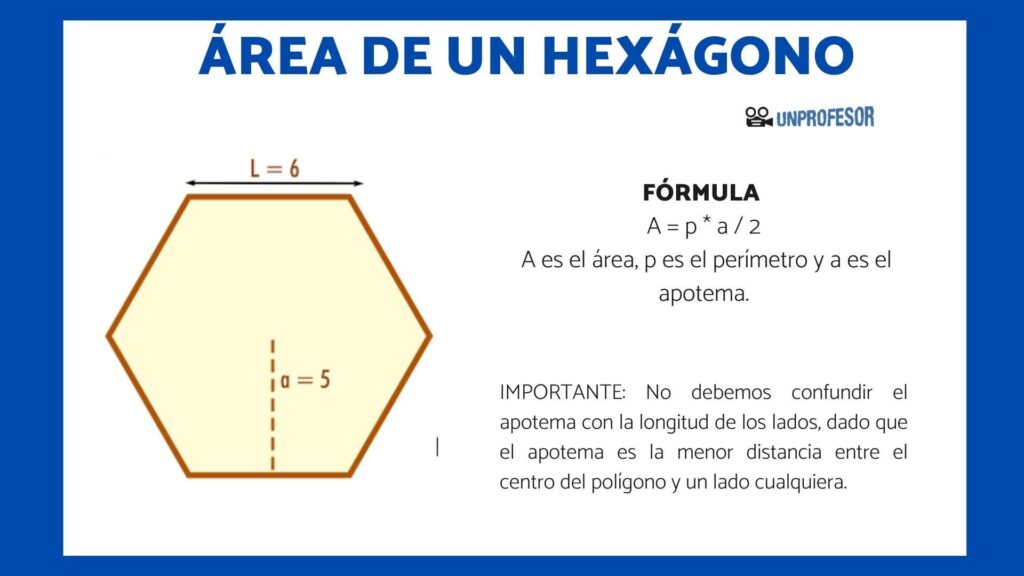
A hexagono can be subdivided into six equilateral triangles, creating a strong and efficient structure. The area and perimeter of a hexagon can be calculated using straightforward formulas:
- Area: Area=332×(side length)2\text{Area} = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \times (\text{side length})^2Area=233×(side length)2
- Perimeter: Perimeter=6×side length\text{Perimeter} = 6 \times \text{side length}Perimeter=6×side length
Tessellation and Symmetry
- Tessellation: The ability to tile a plane without gaps makes hexagons ideal for tiling, paving, and creating intricate patterns.
- Symmetry: Hexagons exhibit both rotational and reflective symmetry, which is a key reason they are widely used in design and art.
Hexagono in Nature: Efficiency and Beauty
Nature has adopted the hexagono as a fundamental structure for its efficiency and strength. This six-sided polygon minimizes material while maximizing space, a quality often described as “nature’s efficiency.”
Examples of Hexagons in Nature
- Beehives: Bees use hexagonal cells to store honey and larvae, as hexagons use the least wax while providing the most storage.
- Snowflakes: Water molecules form hexagonal patterns during crystallization due to the arrangement of hydrogen bonds.
- Basalt Columns: Formed by volcanic activity, hexagonal basalt columns are a testament to the natural tessellation of cooled lava.
Applications of Hexagonal Patterns in Design and Technology
The hexagono is not just a natural wonder; it is a cornerstone of modern design, architecture, and technology. Its unique properties make it a go-to shape for efficient, strong, and aesthetically pleasing designs.
In Architecture and Design
- Hexagonal Tiles: Used in flooring and walls to create seamless and durable surfaces.
- Structural Design: Hexagonal frameworks are common in geodesic domes and bridges due to their strength and load-bearing capabilities.
In Technology
- Engineering: Hexagonal nuts and bolts are standard in mechanical design because of their strength and ease of use.
- Molecular Structures: Benzene, a fundamental organic compound, has a hexagonal arrangement of carbon atoms.
- Crystallography: Hexagonal patterns are common in crystal structures, providing insights into material science.
How to Draw a Perfect Hexagono
Creating a hexagono is simple if you follow precise steps. Whether for geometry classes, design projects, or artistic endeavors, this guide helps you achieve a perfect hexagonal shape.
- Draw a Circle: Start with a circle of your desired radius.
- Mark Six Points: Divide the circumference into six equal parts.
- Connect the Points: Use a ruler to draw straight lines between the marked points.
This method is widely used for creating symmetrical designs and tessellations.
Why Hexagono is a Preferred Shape in Various Industries
The hexagono is a favorite in industries ranging from construction to aerospace. Its ability to distribute force evenly and create stable structures makes it indispensable.
In Construction
Hexagons are used in honeycomb panels for lightweight yet strong structures. These panels are common in aerospace, automotive, and building industries.
In Energy and Computing
Hexagonal grids are being explored for solar panels and energy-efficient computing grids, thanks to their ability to optimize space and energy distribution.
FAQs
- What is the definition of a hexagono?
A hexagono is a six-sided polygon with equal sides and angles, commonly found in geometry, nature, and design. - Why do bees use hexagonal cells in their hives?
Bees use hexagonal cells because they maximize storage space while minimizing the wax required, showcasing nature’s efficiency. - How do hexagons tessellate?
Hexagons tessellate perfectly because their angles (120 degrees) allow them to fit together without gaps, making them ideal for tiling and patterns. - What are some practical uses of hexagons?
Hexagons are used in tiling, engineering, molecular structures, and architecture for their strength, symmetry, and efficiency. - Why are hexagons significant in technology?
Hexagons are crucial in technology due to their use in molecular chemistry, crystallography, and energy-efficient grid designs.






